Updated February 14, 2026
Reading Time: 4 minutes
Modernizing Link Building
Originally launched in April 2012, Google’s Penguin algorithm update targeted websites that engaged in manipulative link-building practices. Unlike its algorithm counterpart, Google Panda, which aimed to weed out low-quality content, Penguin focused on the quality of backlinks. Penguin emphasized the importance of a natural, high-quality link profile as an SEO strategy.
In this guide, we’ll explore Google Penguin’s history, core features, and its impact on today’s SEO practices.
Key Features
The Google Penguin Algorithm introduced several crucial changes to ranking websites based on their backlink profiles. Here are the key features:
- Focus on Link Quality Over Quantity
Penguin’s core principle was to prioritize the quality of links pointing to a website rather than the sheer number of links. Back in 2012, it was a common Grey Hat SEO practice to create empty listings on all types of directories and link farms to generate backlinks. To combat this “noise,” Google Penguin evaluated each link’s relevance, authority, and authenticity to ensure only natural and valuable links contributed to a site’s SEO ranking. High-quality links were defined as inbound links from reputable, relevant websites that provide real value to users. Focusing on link quality over quantity encouraged web admins to build genuine connections and steer clear of manipulative tactics.
- Penalization for Manipulative Practices
The Penguin algorithm penalized websites using “unnatural” or manipulative link-building practices. These manipulative tactics include buying links, participating in link farms, or using automated programs to generate backlinks. When Penguin detects an unnatural link profile, it reduces the site’s search rankings, making it harder for it to appear in top search results. In particularly bad cases, a site can receive a manual penalty that removes it from all search results. Penguin was designed as a deterrent against grey- and black-hat SEO techniques and to reward sites using ethical link-building strategies.
Evolution of Google Penguin Updates
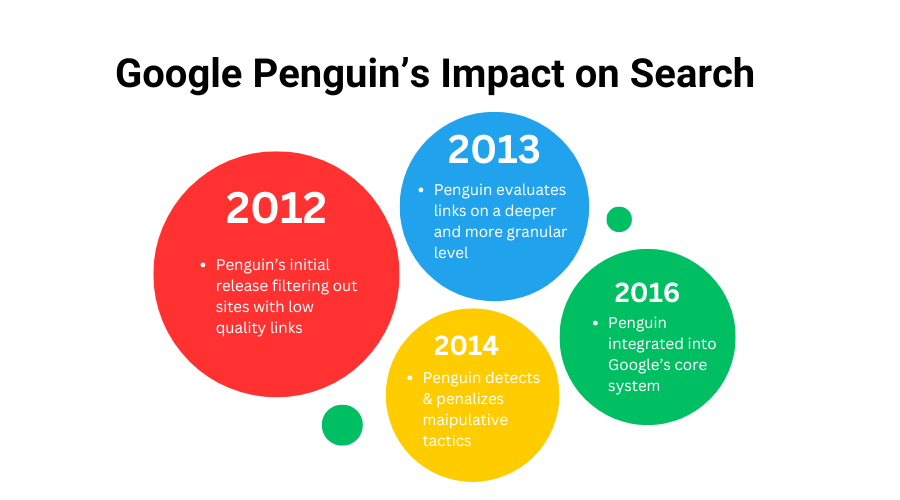
The Penguin Algorithm has undergone multiple updates since its initial release. Each new version refined its identification of link quality as well as the depth of link penalties. Here’s how Penguin evolved over time:
- Penguin 1.0 (April 2012)
The initial release of the Penguin Algorithm targeted websites using spammy link-building practices. It aimed to improve search results by filtering out sites with low-quality, manipulative links.
- Penguin 2.0 (May 2013)
The Penguin 2.0 update affected approximately 2.3% of English-US queries. Yet, it had a worldwide impact. Penguin targeted advertorials that violated Google’s quality guidelines and improved the detection of hacked sites. 2.0 affected more websites and was more comprehensive in its assessment.
- Penguin 3.0 (October 2014)
Penguin 3.0 further refined the link-related algorithm, making it more effective at detecting and penalizing manipulative practices. Additionally, the update enabled quicker recovery for sites that improved their link profiles.
- Penguin 4.0 (September 2016)
In September 2016, Google announced that the Penguin Algorithm had become part of its core search engine algorithm. Penguin 4.0 was the most significant and far-reaching update. This version allowed for more immediate link assessments, rewarding sites that improved their link profiles while demoting rankings for sites that didn’t comply with Google’s link guidelines. This real-time update also facilitated a better feedback loop with webmasters.
Link Building & Guest Blogging in the Post-Penguin Era
The Penguin updates have profoundly reshaped strategies around link-building and guest blogging, emphasizing ethical practices and quality over quantity. If you haven’t familiarized yourself with Google Search Essentials (formerly webmaster quality guidelines), it’s a must-read for SEO.
- Effective link building now requires establishing relationships with relevant businesses or industries. Gone are the days of creating directory profiles just for the sake of a backlink. The search algorithm is looking for natural link profiles that reflect backlinks from related websites. What’s the upshot? Beware of digital marketing agencies offering link-building services from sites unrelated to your industry.
- Once a common method for gaining backlinks, guest blogging has evolved significantly. Following Google Penguin updates, it’s crucial to avoid manipulative schemes by ensuring content is unique, relevant, and transparently aligned with industry standards. Guest blogging contributions should be informative and unique, relevant to your industry, and made in partnership with legitimate sites. Clear disclosures of the author’s relationship (and financial affiliation) with the host site are essential for transparency.
Impact on SEO Practices
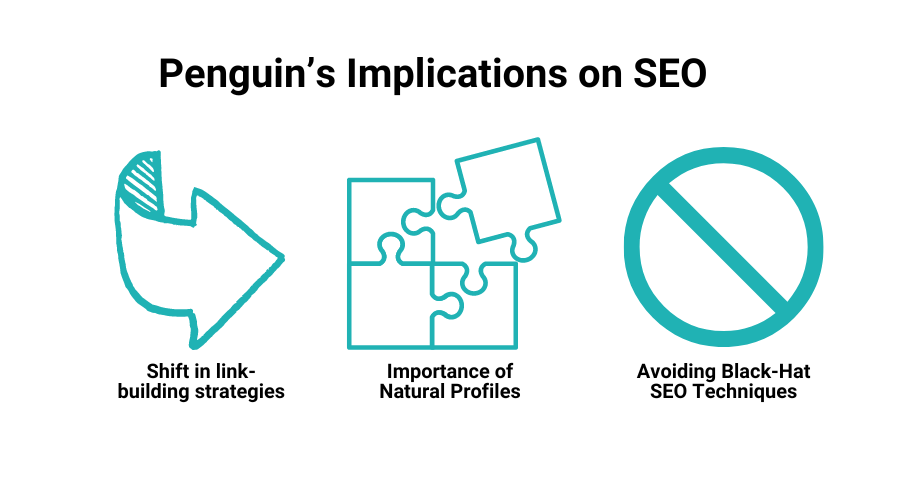
- Shift in Link-Building Strategies
Before Penguin, many SEO practitioners focused on acquiring as many links as possible. They often resorted to questionable tactics like link farms, irrelevant directories, and paying for backlinks. Post-Penguin, there has been a clear shift towards quality over quantity. SEO professionals now prioritize obtaining links from reputable, relevant sources that provide real value to users. Penguin’s shift has led to more sustainable and ethical link-building practices.
- Importance of Natural Link Profiles
Penguin emphasized the need for natural link profiles built organically rather than through manipulative practices. Links should be acquired through genuine relationships, valuable content, and user engagement. Google clearly shows a preference for authenticity in link-building practices. Natural link profiles are characterized by diversity in link sources, anchor text, and link placement, all reflecting a real and varied web presence.
- Avoiding Black-Hat SEO Techniques
The Penguin update’s penalties for manipulative link-building have clarified that grey- and black-hat SEO techniques are no longer viable. Strategies such as buying backlinks, participating in link schemes, and using automated tools for link generation are hazardous and likely to result in penalties. Successful SEO practitioners have moved towards link-building techniques that focus on real business relationships, sustainable growth, and compliance with Google’s guidelines.
The Future of Google Penguin
The Google Penguin Algorithm profoundly transformed the SEO landscape by emphasizing the importance of link quality over quantity and penalizing manipulative practices. Its integration into Google’s core algorithm underscores the need for continuous, real-time compliance with SEO best practices.
By understanding Penguin’s key features and significant updates and adapting to the shift in link-building strategies, you can ensure that your website remains competitive and compliant. Prioritizing a natural link profile will help you build a sustainable website’s visibility in search.
Don’t have the time or inclination to manage your backlink profile? We can help you set yourself up for long-term SEO success.
 Mastering Meta Descriptions: Best Practices, Examples, and Insights
Mastering Meta Descriptions: Best Practices, Examples, and Insights